本文主要是介紹Android中實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗的的正確姿勢,如果你在實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗時(shí)遇到了一些問題,那么請仔細(xì)閱讀本文,相信文章會對你有所幫助。
收獲早知道
閱讀完本文后,你可以有以下收獲
實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗的方式
由于本人水平有限,只知道一下幾種實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗的方式
下面,就利用以上三種方式分別實(shí)現(xiàn)Android中的底部彈窗。
利用PopWindow實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗
因?yàn)楸疚闹饕墙榻B實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗的方式,所以,不會對PopupWindow進(jìn)行具體的講解,大家可以到這里了解PopupWindow。
直接進(jìn)入主題,按照套路,一步步實(shí)現(xiàn)利用PopupWindow實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗。首先,寫一個(gè)布局文件作為PopupWindow中的內(nèi)容,布局文件如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:background="#553b3a3a" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:orientation="vertical" android:id="@+id/content" android:background="@android:color/white" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:textColor="#333" android:text="相機(jī)" android:padding="8dp" android:id="@+id/open_from_camera" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="15sp" android:layout_height="40dp" /> <TextView android:layout_marginTop="1dp" android:id="@+id/open_album" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:textColor="#333" android:text="打開圖庫" android:padding="8dp" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="15sp" android:layout_height="40dp" /> <TextView android:layout_marginTop="1dp" android:id="@+id/cancel" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:textColor="#333" android:text="取消" android:padding="8dp" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="15sp" android:layout_height="40dp" /> </LinearLayout></RelativeLayout>
注:這里使用的是填充父窗口的方式,如果不這樣做的話,就不能看出遮住后面的效果,看下圖更容易理解,左圖為填充父布局的方式,右圖為
自適應(yīng)的方式

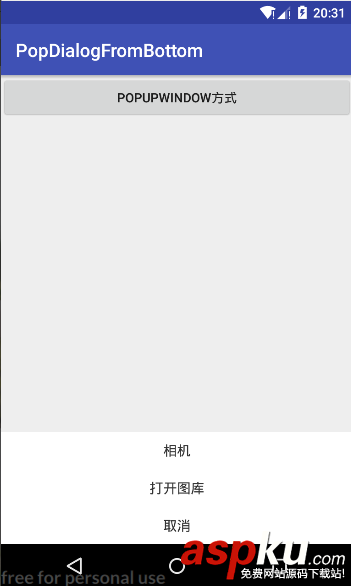
注:因?yàn)椴捎锰畛涓覆季值姆绞剑@里彈出的窗口都是PopupWindow,所以點(diǎn)擊左圖中的陰影彈窗不會消失,因?yàn)殛幱耙彩荘opupWindow呀!解決方法就是,把左圖中的陰影部分用一個(gè)TextView控件填充,然后為這個(gè)TextView設(shè)置點(diǎn)擊事件,點(diǎn)擊TextView時(shí)讓PopupWindow消失就行了。
下面看下利用PopupWindow實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗的代碼,重要的方法我會具體講解
private void initPopupWindow() { //要在布局中顯示的布局 contentView = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.popup_layout, null, false); //實(shí)例化PopupWindow并設(shè)置寬高 popupWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT); popupWindow.setBackgroundDrawable(new BitmapDrawable()); //點(diǎn)擊外部消失,這里因?yàn)镻opupWindow填充了整個(gè)窗口,所以這句代碼就沒用了 popupWindow.setOutsideTouchable(true); //設(shè)置可以點(diǎn)擊 popupWindow.setTouchable(true); //進(jìn)入退出的動畫 popupWindow.setAnimationStyle(R.style.MyPopWindowAnim); } private void showPopWindow() { View rootview = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.activity_main, null); popupWindow.showAtLocation(rootview, Gravity.BOTTOM, 0, 0); }重點(diǎn)看一下這句代碼
popupWindow.showAtLocation(rootview, Gravity.BOTTOM, 0, 0);
這句代碼是設(shè)置彈出窗口從哪里彈出, void showAtLocation (View parent,int gravity,int x,int y) 方法有四個(gè)參數(shù),第一個(gè)參數(shù)是父布局,第二個(gè)為從父布局的哪里彈出,x和y是相對于父布局彈出位置的偏移量。由于,我們要將mPopWindow放在整個(gè)屏幕的最低部,所以我們將R.layout.activity_main做為它的父容器,將其顯示在BOTTOM的位置。
再仔細(xì)看下上圖,利用PopupWindow實(shí)現(xiàn)從底部的彈窗并不能覆蓋到狀態(tài)欄,下面就來解決這個(gè)問題。
解決PopupWindow彈出的窗口不能覆蓋狀態(tài)欄問題
想要覆蓋到狀態(tài)欄還需要添以下代碼
//彈出的窗口是否覆蓋狀態(tài)欄 public void fitPopupWindowOverStatusBar(boolean needFullScreen) { if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) { try { //利用反射重新設(shè)置mLayoutInScreen的值,當(dāng)mLayoutInScreen為true時(shí)則PopupWindow覆蓋全屏。 Field mLayoutInScreen = PopupWindow.class.getDeclaredField("mLayoutInScreen"); mLayoutInScreen.setAccessible(true); mLayoutInScreen.set(popupWindow, needFullScreen); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }再改變一下顯示PopupWindow的代碼,如下
//設(shè)置是否遮住狀態(tài)欄 fitPopupWindowOverStatusBar(true); View rootview = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.activity_main, null); popupWindow.showAtLocation(rootview, Gravity.BOTTOM, 0, 0);
再看下效果
好了,到此完美解決問題,可以發(fā)現(xiàn)利用PopupWindow實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗其實(shí)還是挺麻煩的。

利用Dialog實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗
先看下代碼,然后在講解
public class DialogFromBottom extends Dialog{ private final static int mAnimationDuration = 200; // 持有 ContentView,為了做動畫 private View mContentView; private boolean mIsAnimating = false; private OnBottomSheetShowListener mOnBottomSheetShowListener; public DialogFromBottom(@NonNull Context context) { super(context, R.style.AppTheme_BottomSheet); } @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); getWindow().getDecorView().setPadding(0, 0, 0, 0); // 在底部,寬度撐滿 WindowManager.LayoutParams params = getWindow().getAttributes(); params.height = ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT; params.gravity = Gravity.BOTTOM | Gravity.CENTER;//dialog從哪里彈出 //彈出窗口的寬高 int screenWidth = QMUIDisplayHelper.getScreenWidth(getContext()); int screenHeight = QMUIDisplayHelper.getScreenHeight(getContext()); params.width = screenWidth < screenHeight ? screenWidth : screenHeight; getWindow().setAttributes(params); setCanceledOnTouchOutside(true); } //設(shè)置彈出dialog中的layout @Override public void setContentView(int layoutResID) { mContentView = LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(layoutResID, null); super.setContentView(mContentView); } @Override public void setContentView(@NonNull View view) { mContentView = view; super.setContentView(view); } @Override public void setContentView(@NonNull View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) { mContentView = view; super.setContentView(view, params); } /** * BottomSheet升起動畫 */ private void animateUp() { if (mContentView == null) { return; } TranslateAnimation translate = new TranslateAnimation( Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 1f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0f ); AlphaAnimation alpha = new AlphaAnimation(0, 1); AnimationSet set = new AnimationSet(true); set.addAnimation(translate); set.addAnimation(alpha); set.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator()); set.setDuration(mAnimationDuration); set.setFillAfter(true); mContentView.startAnimation(set); } /** * BottomSheet降下動畫 */ private void animateDown() { if (mContentView == null) { return; } TranslateAnimation translate = new TranslateAnimation( Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 1f ); AlphaAnimation alpha = new AlphaAnimation(1, 0); AnimationSet set = new AnimationSet(true); set.addAnimation(translate); set.addAnimation(alpha); set.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator()); set.setDuration(mAnimationDuration); set.setFillAfter(true); set.setAnimationListener(new Animation.AnimationListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) { mIsAnimating = true; } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) { mIsAnimating = false; /** * Bugfix: Attempting to destroy the window while drawing! */ mContentView.post(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { // java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: View=com.android.internal.policy.PhoneWindow$DecorView{22dbf5b V.E...... R......D 0,0-1080,1083} not attached to window manager // 在dismiss的時(shí)候可能已經(jīng)detach了,簡單try-catch一下 try { DialogFromBottom.super.dismiss(); } catch (Exception e) { //這里處理異常 } } }); } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) { } }); mContentView.startAnimation(set); } @Override public void show() { super.show(); animateUp(); if (mOnBottomSheetShowListener != null) { mOnBottomSheetShowListener.onShow(); } } @Override public void dismiss() { if (mIsAnimating) { return; } animateDown(); } public interface OnBottomSheetShowListener { void onShow(); }}額,代碼有點(diǎn)長,其實(shí)很容易理解,這里主要說下onCreate方法中的內(nèi)容,可以仔細(xì)看下注釋。
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); getWindow().getDecorView().setPadding(0, 0, 0, 0);//把父布局的padding都設(shè)為0,目的是可以dialog撐滿全屏。 // 在底部,寬度撐滿 WindowManager.LayoutParams params = getWindow().getAttributes(); params.height = ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT; params.gravity = Gravity.BOTTOM | Gravity.CENTER;//dialog從底部彈出 //彈出窗口的寬高,DisplayHelper.getScreenWidth(getContext());和DisplayHelper.getScreenHeight(getContext());是拿到屏幕的寬高。 int screenWidth = DisplayHelper.getScreenWidth(getContext()); int screenHeight = DisplayHelper.getScreenHeight(getContext()); params.width = screenWidth < screenHeight ? screenWidth : screenHeight;//適配手機(jī)橫屏 getWindow().setAttributes(params);//重新設(shè)置dialog的屬性 setCanceledOnTouchOutside(true);//設(shè)置觸摸dialog以外,dialog是否消失 }利用Dialog實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗就是繼承系統(tǒng)Dialog然后重寫了onCreate方法,設(shè)置dialog從底部彈出。因?yàn)槭抢^承Dialog,所以有Dialog的特性,既觸摸底部彈窗以外的部分,彈窗會自動消失,這里就不在演示,可以在文末獲取源碼,自己實(shí)驗(yàn)一下就知道了。
利用DialogFragment實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗
在實(shí)現(xiàn)彈窗之前,先了解一下DialogFragment
DialogFragment在android 3.0時(shí)被引入。是一種特殊的Fragment,用于在Activity的內(nèi)容之上展示一個(gè)模態(tài)的對話框。
使用DialogFragment至少需要實(shí)現(xiàn)onCreateView或者onCreateDIalog方法。onCreateView即使用定義的xml布局文件展示Dialog。onCreateDialog即利用AlertDialog或者Dialog創(chuàng)建出Dialog。下面通過實(shí)現(xiàn)onCreateView方法來實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗。
@Nullable @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog_layout, container, false); return view; } @Override public void onStart() { super.onStart(); initParams();//初始化彈窗的參數(shù) } private void initParams() { Window window = getDialog().getWindow(); if (window != null) { WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = window.getAttributes(); //調(diào)節(jié)灰色背景透明度[0-1],默認(rèn)0.5f lp.dimAmount = dimAmount; //是否在底部顯示 if (showBottom) { lp.gravity = Gravity.BOTTOM; if (animStyle == 0) { animStyle = R.style.DefaultAnimation; } } //設(shè)置dialog寬度 if (width == 0) { lp.width = DisplayHelper.getScreenWidth(getActivity()) - 2 * DisplayHelper.dp2px(getActivity(), margin); } else { lp.width = DisplayHelper.dp2px(getActivity(), width); } //設(shè)置dialog高度 if (height == 0) { lp.height = WindowManager.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT; } else { lp.height = DisplayHelper.dp2px(getActivity(), height); } //設(shè)置dialog進(jìn)入、退出的動畫 window.setWindowAnimations(animStyle); window.setAttributes(lp); } setCancelable(outCancel);//設(shè)置點(diǎn)擊外部是否消失 }因?yàn)镈ialogFragment也是Fragment,所以,DialogFragment有和Fragment一樣的生命周期,在onStart方法中初始化彈窗的數(shù)據(jù),在onCreateView中加載布局,同樣,和Fragment使用方法也是一樣的,下面看下在Activity中的使用
void showDialog() { FragmentTransaction ft = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction(); // Create and show the dialog. DialogFragmentFromBottom newFragment = new DialogFragmentFromBottom(); newFragment.show(ft, "dialog"); }結(jié)束語
好了,到這里三種實(shí)現(xiàn)底部彈窗的方式已經(jīng)講完了,大家可以下載源碼研究一下, 源碼在這里 ,在做項(xiàng)目時(shí)選擇最適合的就好,在這里還是推薦使用DialogFragment,這種方式可定制性很高,實(shí)現(xiàn)彈窗的方式也比較優(yōu)雅。
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望對大家的學(xué)習(xí)有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林網(wǎng)。
新聞熱點(diǎn)
疑難解答
圖片精選