前言
很多公司考慮到安全問題,項目中都采用https加密協(xié)議進行數(shù)據(jù)傳輸。但是一些公司又不想花一筆錢去CA申請證書,所以就采用自簽名的證書。
OkHttp默認是可以訪問通過CA認證的HTTPS鏈接,例如百度首頁也是https鏈接(https://www.baidu.com/)。但是如果是你們公司自簽名(即自己用keytool生成的證書,而不是采用通過CA認證的證書)的服務(wù)器,OkHttp是無法訪問的,例如訪問12306網(wǎng)站(https://kyfw.12306.cn/otn/),會報如下錯誤:

HTTPS的工作原理
HTTPS在傳輸數(shù)據(jù)之前需要客戶端(瀏覽器)與服務(wù)端(網(wǎng)站)之間進行一次握手,在握手過程中將確立雙方加密傳輸數(shù)據(jù)的密碼信息。握手過程的簡單描述如下:
握手過程中如果有任何錯誤,都會使加密連接斷開,從而阻止了隱私信息的傳輸。
使用OKHTTP請求自簽名的https服務(wù)器數(shù)據(jù)
以下我們使用12306網(wǎng)站為例
1. 首先去12306網(wǎng)站首頁下載證書 http://www.12306.cn/
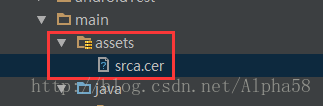
2. 將下載的證書srca.cer放到工程的assets文件夾下。
3. 添加HTTPS工具類
package com.alpha58.okhttp;import android/70237.html">android.content.Context;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.security.GeneralSecurityException;import java.security.KeyStore;import java.security.cert.Certificate;import java.security.cert.CertificateFactory;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.Collection;import javax.net.ssl.KeyManagerFactory;import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager;import javax.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactory;import javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager;import okhttp3.OkHttpClient;/** * Created by admin on 2017/03/12. */public final class HTTPSUtils { private OkHttpClient client; public Context mContext; /** * 獲取OkHttpClient實例 * @return */ public OkHttpClient getInstance() { return client; } /** * 初始化HTTPS,添加信任證書 * @param context */ public HTTPSUtils(Context context) { mContext = context; X509TrustManager trustManager; SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory; final InputStream inputStream; try { inputStream = mContext.getAssets().open("srca.cer"); // 得到證書的輸入流 try { trustManager = trustManagerForCertificates(inputStream);//以流的方式讀入證書 SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS"); sslContext.init(null, new TrustManager[]{trustManager}, null); sslSocketFactory = sslContext.getSocketFactory(); } catch (GeneralSecurityException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } client = new OkHttpClient.Builder() .sslSocketFactory(sslSocketFactory, trustManager) .build(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 以流的方式添加信任證書 */ /** * Returns a trust manager that trusts {@code certificates} and none other. HTTPS services whose * certificates have not been signed by these certificates will fail with a {@code * SSLHandshakeException}. * <p> * <p>This can be used to replace the host platform's built-in trusted certificates with a custom * set. This is useful in development where certificate authority-trusted certificates aren't * available. Or in production, to avoid reliance on third-party certificate authorities. * <p> * <p> * <h3>Warning: Customizing Trusted Certificates is Dangerous!</h3> * <p> * <p>Relying on your own trusted certificates limits your server team's ability to update their * TLS certificates. By installing a specific set of trusted certificates, you take on additional * operational complexity and limit your ability to migrate between certificate authorities. Do * not use custom trusted certificates in production without the blessing of your server's TLS * administrator. */ private X509TrustManager trustManagerForCertificates(InputStream in) throws GeneralSecurityException { CertificateFactory certificateFactory = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509"); Collection<? extends Certificate> certificates = certificateFactory.generateCertificates(in); if (certificates.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("expected non-empty set of trusted certificates"); } // Put the certificates a key store. char[] password = "password".toCharArray(); // Any password will work. KeyStore keyStore = newEmptyKeyStore(password); int index = 0; for (Certificate certificate : certificates) { String certificateAlias = Integer.toString(index++); keyStore.setCertificateEntry(certificateAlias, certificate); } // Use it to build an X509 trust manager. KeyManagerFactory keyManagerFactory = KeyManagerFactory.getInstance( KeyManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm()); keyManagerFactory.init(keyStore, password); TrustManagerFactory trustManagerFactory = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance( TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm()); trustManagerFactory.init(keyStore); TrustManager[] trustManagers = trustManagerFactory.getTrustManagers(); if (trustManagers.length != 1 || !(trustManagers[0] instanceof X509TrustManager)) { throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected default trust managers:" + Arrays.toString(trustManagers)); } return (X509TrustManager) trustManagers[0]; } /** * 添加password * @param password * @return * @throws GeneralSecurityException */ private KeyStore newEmptyKeyStore(char[] password) throws GeneralSecurityException { try { KeyStore keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance(KeyStore.getDefaultType()); // 這里添加自定義的密碼,默認 InputStream in = null; // By convention, 'null' creates an empty key store. keyStore.load(in, password); return keyStore; } catch (IOException e) { throw new AssertionError(e); } }}4.代碼中請求
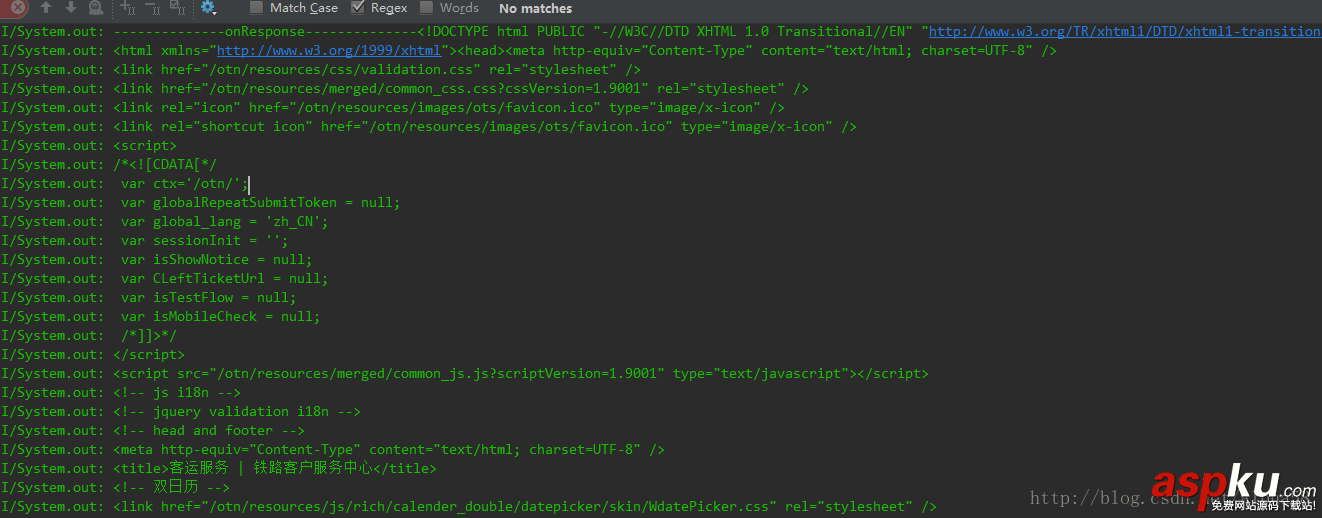
public void getHttpsHtml(View view) { Request request = new Request.Builder() .url("https://kyfw.12306.cn/otn/") .build(); HTTPSUtils httpsUtils = new HTTPSUtils(this); httpsUtils.getInstance().newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() { @Override public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) { System.out.println("--------------onFailure--------------" + e.toString()); } @Override public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException { System.out.println("--------------onResponse--------------" + response.body().string()); } }); } 5. 最后能打印出這些信息就說明請求成功啦!
注意:別忘了加權(quán)限和依賴okhttp庫
Demo地址:https://github.com/Alpha58/okhttps
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望對大家的學(xué)習(xí)有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林網(wǎng)。
新聞熱點
疑難解答
圖片精選