以下分別通過Context認知角度,繼承關系,對象創建等方面android中Context做了深入的解釋,一起學習下。
1、Context認知。
Context譯為場景,一個應用程序可以認為是一個工作環境,在這個工作環境中可以存在許多場景,coding代碼的場景 ,打電話的場景,開會的場景。這些場景可以類比不同的Activity,service。
2、從兩個角度認識Context。
第一:Activity繼承自Context,同時Activity還實現了其他的interface,我們可以這樣看,activity在語法上extends了Context,其本質上是一個Context,但同時其實現了許多interface,擴充了Context的功能,擴充之后的類成為Activity或者Service。
第二:Context本質上包含了場景的所有元素,故而設定其為abstract,Activity和Service繼承自Context,它們本質上可以認為就是Context。
3、Context繼承關系圖
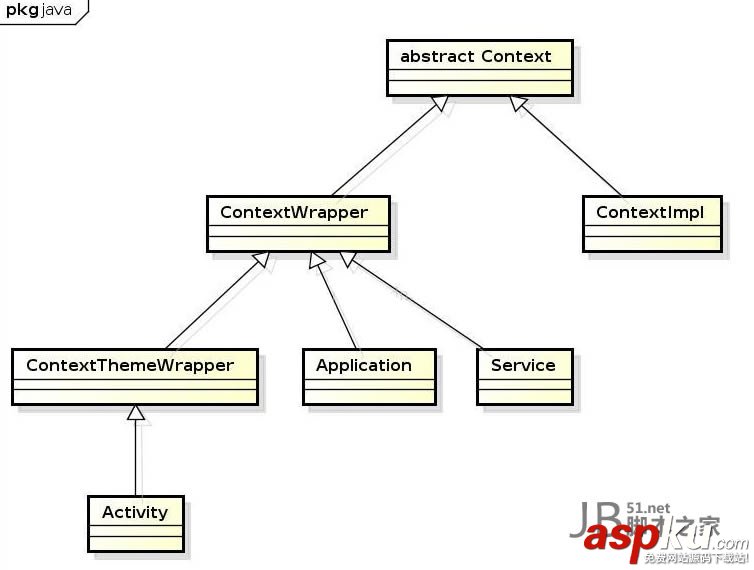
4、Application對象的ContextImpl對象創建過程。
step 1、Ams通過遠程Binder調用ActivityThread的內部類ApplicationThread的bingApplication方法,參數包括ApplicationInfo,這個對象由Ams創建,通過IPC傳遞到ActivityThread的內部類ApplicationThread中。
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo, List<ProviderInfo> providers, ComponentName instrumentationName, String profileFile, ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, boolean autoStopProfiler, Bundle instrumentationArgs, IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher, int debugMode, boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map<String, IBinder> services, Bundle coreSettings) { if (services != null) { // Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services); } setCoreSettings(coreSettings); AppBindData data = new AppBindData(); data.processName = processName; data.appInfo = appInfo; data.providers = providers; data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName; data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs; data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher; data.debugMode = debugMode; data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode; data.persistent = persistent; data.config = config; data.compatInfo = compatInfo; data.initProfileFile = profileFile; data.initProfileFd = profileFd; data.initAutoStopProfiler = false; queueOrSendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data); } step 2、構建AppBindData對象,如上代碼所示。
step 3、調用H Handler,執行handleBindApplication()方法。
static final class AppBindData { LoadedApk info; String processName; ApplicationInfo appInfo; List<ProviderInfo> providers; ComponentName instrumentationName; Bundle instrumentationArgs; IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher; int debugMode; boolean restrictedBackupMode; boolean persistent; Configuration config; CompatibilityInfo compatInfo; /** Initial values for {@link Profiler}. */ String initProfileFile; ParcelFileDescriptor initProfileFd; boolean initAutoStopProfiler; public String toString() { return "AppBindData{appInfo=" + appInfo + "}"; } } private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) { mBoundApplication = data; mConfiguration = new Configuration(data.config); mCompatConfiguration = new Configuration(data.config); //.......... TimeZone.setDefault(null); /* * Initialize the default locale in this process for the reasons we set the time zone. */ Locale.setDefault(data.config.locale); data.info = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.appInfo, data.compatInfo);//data.info對象為LoadApk,此時data.info為null,使用getPackageINfoNoCheck創建此對象。 if (data.instrumentationName != null) {//該條件盡在Android Unit Test工程時會執行到,此處直接看else語句 ContextImpl appContext = new ContextImpl(); appContext.init(data.info, null, this); InstrumentationInfo ii = null; try { ii = appContext.getPackageManager(). getInstrumentationInfo(data.instrumentationName, 0); } catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) { } if (ii == null) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to find instrumentation info for: " + data.instrumentationName); } mInstrumentationAppDir = ii.sourceDir; mInstrumentationAppPackage = ii.packageName; mInstrumentedAppDir = data.info.getAppDir(); ApplicationInfo instrApp = new ApplicationInfo(); instrApp.packageName = ii.packageName; instrApp.sourceDir = ii.sourceDir; instrApp.publicSourceDir = ii.publicSourceDir; instrApp.dataDir = ii.dataDir; instrApp.nativeLibraryDir = ii.nativeLibraryDir; LoadedApk pi = getPackageInfo(instrApp, data.compatInfo, appContext.getClassLoader(), false, true); ContextImpl instrContext = new ContextImpl(); instrContext.init(pi, null, this); try { java.lang.ClassLoader cl = instrContext.getClassLoader(); mInstrumentation = (Instrumentation) cl.loadClass(data.instrumentationName.getClassName()).newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to instantiate instrumentation " + data.instrumentationName + ": " + e.toString(), e); } mInstrumentation.init(this, instrContext, appContext, new ComponentName(ii.packageName, ii.name), data.instrumentationWatcher); if (mProfiler.profileFile != null && !ii.handleProfiling && mProfiler.profileFd == null) { mProfiler.handlingProfiling = true; File file = new File(mProfiler.profileFile); file.getParentFile().mkdirs(); Debug.startMethodTracing(file.toString(), 8 * 1024 * 1024); } try { mInstrumentation.onCreate(data.instrumentationArgs); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException( "Exception thrown in onCreate() of " + data.instrumentationName + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } else { mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();//初始化Instrumentation對象,一個應用程序對應一個Instrumentation對象 } Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null); mInitialApplication = app; try { mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);//調用Application程序都應的onCreate方法。 } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } }第三步可以又可以分為三小步。
step 3.1、給AppBindData的info變量賦值。
data.info = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.appInfo, data.compatInfo);//data.info對象為LoadApk,此時data.info為null,使用getPackageINfoNoCheck創建此對象。
step 3.2、初始化Instrumentation對象。
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();//初始化Instrumentation對象,一個應用程序對應一個Instrumentation對象
step 3.3、創建Application對象。
Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
我們著重看一下step 3.1和step3.3.
step 3.1:mPackages和mResourcePackages集合,以packageName為key值,我們知道一個應用程序中的packageName是相同的,也就是說,此處一旦創建,其他地方再次調用此函數,就不需要創建了。總結:也就是說一個應用程序中的LoadedApk對象是唯一的。此處的LoadedApk,也被稱為packageInfo。
public final LoadedApk getPackageInfoNoCheck(ApplicationInfo ai, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo) { return getPackageInfo(ai, compatInfo, null, false, true); } private LoadedApk getPackageInfo(ApplicationInfo aInfo, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, ClassLoader baseLoader, boolean securityViolation, boolean includeCode) {/*includeCode 默認為true*/ synchronized (mPackages) { WeakReference<LoadedApk> ref; if (includeCode) {//1、首先從mPackages或者mResourcePackages 集合中以packageName為Key值,獲取LoadApk對象。 ref = mPackages.get(aInfo.packageName); } else { ref = mResourcePackages.get(aInfo.packageName); } LoadedApk packageInfo = ref != null ? ref.get() : null; if (packageInfo == null || (packageInfo.mResources != null && !packageInfo.mResources.getAssets().isUpToDate())) { if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, (includeCode ? "Loading code package " : "Loading resource-only package ") + aInfo.packageName + " (in " + (mBoundApplication != null ? mBoundApplication.processName : null) + ")"); packageInfo = new LoadedApk(this, aInfo, compatInfo, this, baseLoader, securityViolation, includeCode && (aInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HAS_CODE) != 0);//2、如果packageInfo對象為null,則new初始化此對象 if (includeCode) {//3、最后將創建的此packageInfo對象,加入到mPackages或者mResourcePackages集合中。 mPackages.put(aInfo.packageName, new WeakReference<LoadedApk>(packageInfo)); } else { mResourcePackages.put(aInfo.packageName, new WeakReference<LoadedApk>(packageInfo)); } } return packageInfo; } }step 3.3、總結:每個應用程序都存在一個Application,用戶可以在AndroidManifest中重寫它,如果不重寫也存在一個默認的Application對象。
framework/base/core/java/android/app/LoadedApk.java
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass, Instrumentation instrumentation) { if (mApplication != null) { return mApplication; } Application app = null; String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className; if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null)) { appClass = "android.app.Application";//1、每個工程都存在一個Application對象,默認的Application對象為android.app.Application,客戶端可以重寫 } try { java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader(); ContextImpl appContext = new ContextImpl();//2、創建ContextImpl對象,這才是Context的實際實現類 appContext.init(this, null, mActivityThread);//3、執行ContextImpl對象的init方法,initResource等對象 app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(//4、以appContext為參數得到Application對象。 cl, appClass, appContext); appContext.setOuterContext(app); } catch (Exception e) { if (!mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to instantiate application " + appClass + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);//5、將創建的Application對象,加入到A來了Application中。 mApplication = app; if (instrumentation != null) {//6、此時的instrumentation為null。 try { instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app); } catch (Exception e) { if (!instrumentation.onException(app, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } } return app; }5、Activity中Context的創建過程
step 1、Ams通過遠程Binder調用ActivityThread的Application的scheduleLaunchActivity方法,參數包括ActivityInfo,這個對象由Ams創建,通過IPC傳遞到ActivityThread的內部類ApplicationThread中。
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident, ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Bundle state, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, String profileName, ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, boolean autoStopProfiler) { ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord(); r.token = token; r.ident = ident; r.intent = intent; r.activityInfo = info; r.compatInfo = compatInfo; r.state = state; r.pendingResults = pendingResults; r.pendingIntents = pendingNewIntents; r.startsNotResumed = notResumed; r.isForward = isForward; r.profileFile = profileName; r.profileFd = profileFd; r.autoStopProfiler = autoStopProfiler; updatePendingConfiguration(curConfig); queueOrSendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r); }step 2、構建ActivityClientRecord對象,如上代碼所示。
step 3、調用H Handler,執行handleLaunchActivity()方法。
其中step 3,又可分為10小步。
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) { // System.out.println("##### [" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "] ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(" + r + ")"); ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo; if (r.packageInfo == null) {//1、如果packageInfo為null,則調用getPackageInfo的得到LoadedApk r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo, Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE); } ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent(); if (component == null) { component = r.intent.resolveActivity( mInitialApplication.getPackageManager()); r.intent.setComponent(component); } if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) { component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName, r.activityInfo.targetActivity); } Activity activity = null; try {//2、調用mInstrumentation的newActivity方法,得到Activity對象 java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader(); activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity( cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent); StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass()); r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl); if (r.state != null) { r.state.setClassLoader(cl); } } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to instantiate activity " + component + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } try { Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);//3、獲取Application對象 if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Performing launch of " + r); if (localLOGV) Slog.v( TAG, r + ": app=" + app + ", appName=" + app.getPackageName() + ", pkg=" + r.packageInfo.getPackageName() + ", comp=" + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() + ", dir=" + r.packageInfo.getAppDir()); if (activity != null) {//4、創建ContextImpl對象 ContextImpl appContext = new ContextImpl(); appContext.init(r.packageInfo, r.token, this); appContext.setOuterContext(activity); CharSequence Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration); if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity " + r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config); activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token, r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent, r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config);//5、執行Activity的attach方法,將此ContextImpl對象,設置給Activity,activity會調用attachBaseContext if (customIntent != null) { activity.mIntent = customIntent; } r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null; activity.mStartedActivity = false; int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();//6、設置主題 if (theme != 0) { activity.setTheme(theme); } activity.mCalled = false; mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);//7、執行Activity的onCreate方法 if (!activity.mCalled) { throw new SuperNotCalledException( "Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() + " did not call through to super.onCreate()"); } r.activity = activity; r.stopped = true; if (!r.activity.mFinished) { activity.performStart();//8、執行Activity的onStart方法 r.stopped = false; } if (!r.activity.mFinished) { if (r.state != null) { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);//9、質細膩感onRestoresInstanceState方法 } } if (!r.activity.mFinished) { activity.mCalled = false; mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state); if (!activity.mCalled) { throw new SuperNotCalledException( "Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() + " did not call through to super.onPostCreate()"); } } } r.paused = true; mActivities.put(r.token, r);//10、將包含activity信息集的r對象,也就是ActivityClientRecord,加入到mActivities中,r.token為key值。 } catch (SuperNotCalledException e) { throw e; } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to start activity " + component + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } return activity; }總結:activity的packageInfo對象和application的packageInfo是同一個對象。
6、Service中Context的創建過程
step 1、Ams通過遠程Binder調用ActivityThread的內部類ApplicationThread的scheduleCreateService方法,參數包括serviceInfo,這個對象由Ams創建,通過IPC傳遞到ActivityThread的內部類ApplicationThread中。
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token, ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo) { CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData(); s.token = token; s.info = info; s.compatInfo = compatInfo; queueOrSendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s); }step 2、構建CreateServiceData對象,如上代碼所示。
step 3、調用H Handler,執行handleCreateService()方法。
其中step 3又可分為一下5步。
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) { // If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well // we are back active so skip it. unscheduleGcIdler(); LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck( data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);//1、得到packageInfo,調用getPackageInfoNoCheck Service service = null; try { java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader(); service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } try { if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name); ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl();//2、創建ContextImpl對象 context.init(packageInfo, null, this); Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);//3、得到Application對象 context.setOuterContext(service); service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app, ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());//4、調用service的attach方法,將實例化的ContextImpl設置給Service service.onCreate(); mServices.put(data.token, service);//5、將service對象加入到mService集合中,key值為data.token。 try { ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting( data.token, 0, 0, 0); } catch (RemoteException e) { // nothing to do. } } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to create service " + data.info.name + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } }綜上所述:
1、無論是Application還是Activity、Service,他們的LoadedApk對象都是同一個,或者說packageInfo為同一個對象。
2、在創建ContextImpl對象時,Application和SErvice通過getPackageInfoNoCheck方法,Activity通過getPackageInfo方法得到。
3、一個應用程序中Context的個數 = Activity的數量+Service的數量 +1。這里的1代表Application。
4、應用程序中包含著多個ContextImpl對象,其內部的PackageInfo卻是同一個。這樣設計意味著ContextImpl是一個輕量級類,PackageInfo是一個重量級類,所有和包相關的操作封裝到PackageInfo中,有利于代碼的封裝與隱藏。
class ContextImpl extends Context { private final static String TAG = "ApplicationContext"; private final static boolean DEBUG = false; private static final HashMap<String, SharedPreferencesImpl> sSharedPrefs = new HashMap<String, SharedPreferencesImpl>(); /*package*/ LoadedApk mPackageInfo;以上就是本篇文章的全部內容,希望大家通過學習能夠對Context有更深入的理解。
新聞熱點
疑難解答