前言
我們平時(shí)在開(kāi)發(fā)的時(shí)候,發(fā)起網(wǎng)絡(luò)請(qǐng)求前,會(huì)需要顯示一個(gè)Loading,一般的做法都是在xml布局上添加好Loading,然后在Activity中,setVisibility來(lái)控制Loading的顯示和隱藏,這樣使用起來(lái)就很不方便,因?yàn)槊恳粋€(gè)xml都得引入一個(gè)Loading布局。
而LoadingBar就更好的解決了這個(gè)問(wèn)題
最近設(shè)計(jì)師在外國(guó)的一個(gè)網(wǎng)站上挑了一個(gè)Loading的效果圖,嘗試實(shí)現(xiàn)之后,雖然和原圖有點(diǎn)不太一樣,但是效果還是不錯(cuò)的。難點(diǎn)就是粘連效果的實(shí)現(xiàn),貝塞爾曲線(xiàn)的點(diǎn)點(diǎn)們簡(jiǎn)直要把我折磨死了。
先上效果圖:

實(shí)例代碼
然后是源碼,就是一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單VIew,可以直接放在xml中使用。
package top.greendami.greendami;import android/209837.html">android/243960.html">android.content.Context;import android.graphics.Canvas;import android.graphics.Paint;import android.graphics.Path;import android.support.annotation.Nullable;import android.util.AttributeSet;import android.view.View;/** * Created by GreendaMi on 2017/3/17. */public class PPView extends View { String TAG = "PPView"; //動(dòng)畫(huà)開(kāi)關(guān) boolean isLoading = true; Context mContext; private int mWidth = 100; private int mheight = 100; public int mColor; public Paint mPaint = new Paint(); float time = 0; //小球與中間打球的最遠(yuǎn)距離 float distance = 100; public PPView(Context context) { super(context); mContext = context; } public PPView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); mContext = context; mColor = context.getResources().getColor(R.color.colorPrimary); init(); } private void init() { mPaint.setAntiAlias(true); mPaint.setColor(mColor); } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); //寬度至少是高度的4倍 if (widthSpecSize < 4 * heightSpecSize) { widthSpecSize = 4 * heightSpecSize; } mWidth = widthSpecSize; mheight = heightSpecSize; distance = 1.2f * mheight; setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, heightSpecSize); } @Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); if (isLoading) { //大圓半徑 float bigR = mheight * 0.32f + mheight * 0.03f * Math.abs((float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(time))); float smallR = mheight * 0.22f + mheight * 0.03f * Math.abs((float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(time))); float bigx = (getWidth()) / 2; //畫(huà)中間大圓 canvas.drawCircle(bigx, mheight / 2, bigR, mPaint); float smalx = getSmallCenterX(); //畫(huà)小圓 canvas.drawCircle(smalx, mheight / 2, smallR, mPaint); //畫(huà)鏈接 //小球在右側(cè) if (smalx > bigx) { Path path = new Path(); //上面的貝塞爾曲線(xiàn)的第一個(gè)點(diǎn),在大圓身上 float x1 = bigx + bigR * (float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(time)); float y1 = mheight / 2 - bigR * (float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(time)); if (y1 > mheight / 2 - smallR) { y1 = mheight / 2 - smallR; x1 = bigx + (float) (Math.sqrt(bigR * bigR - smallR * smallR)); } //上面的貝塞爾曲線(xiàn)的第三個(gè)點(diǎn),在小圓身上 float x2 = smalx - smallR * (float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(time)); float y2 = mheight / 2 - smallR * (float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(time)); if (y2 > mheight / 2 - smallR * 0.8) { y2 = mheight / 2 - smallR * 0.8f; x2 = smalx - smallR * (float) (Math.sqrt(1-0.64f)); } //下面的貝塞爾曲線(xiàn)的第三個(gè)點(diǎn),在小圓身上 float x3 = smalx - smallR * (float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(time)); float y3 = mheight / 2 + smallR * (float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(time)); if (y3 < mheight / 2 + smallR * 0.8) { y3 = mheight / 2 + smallR * 0.8f; x3 = smalx - smallR * (float) (Math.sqrt(1-0.64f)); } //下面的貝塞爾曲線(xiàn)的第一個(gè)點(diǎn),在大圓身上 float x4 = bigx + bigR * (float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(time)); float y4 = mheight / 2 + bigR * (float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(time)); if (y4 < mheight / 2 + smallR) { y4 = mheight / 2 + smallR; x4 = bigx + (float) (Math.sqrt(bigR * bigR - smallR * smallR)); } path.moveTo(x1, y1); path.quadTo((bigx + smalx) / 2, mheight / 2, x2, y2); // 繪制貝賽爾曲線(xiàn)(Path) path.lineTo(x3, y3); path.quadTo((bigx + smalx) / 2, mheight / 2, x4, y4); canvas.drawPath(path, mPaint); } //小球在左側(cè) if (smalx < bigx) { Path path = new Path(); float x1 = bigx + bigR * (float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(time)); float y1 = mheight / 2 - bigR * (float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(time)); if (y1 > mheight / 2 - smallR) { y1 = mheight / 2 - smallR; x1 = bigx - (float) (Math.sqrt(bigR * bigR - smallR * smallR)); } float x2 = smalx - smallR * (float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(time)); float y2 = mheight / 2 - smallR * (float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(time)); if (y2 > mheight / 2 - smallR * 0.8) { y2 = mheight / 2 - smallR * 0.8f; x2 = smalx + smallR * (float) (Math.sqrt(1-0.64f)); } float x3 = smalx - smallR * (float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(time)); float y3 = mheight / 2 + smallR * (float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(time)); if (y3 < mheight / 2 + smallR * 0.8) { y3 = mheight / 2 + smallR * 0.8f; x3 = smalx + smallR * (float) (Math.sqrt(1-0.64f)); } float x4 = bigx + bigR * (float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(time)); float y4 = mheight / 2 + bigR * (float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(time)); if (y4 < mheight / 2 + smallR) { y4 = mheight / 2 + smallR; x4 = bigx - (float) (Math.sqrt(bigR * bigR - smallR * smallR)); } path.moveTo(x1, y1); path.quadTo((bigx + smalx) / 2, mheight / 2, x2, y2); // 繪制貝賽爾曲線(xiàn)(Path) path.lineTo(x3, y3); path.quadTo((bigx + smalx) / 2, mheight / 2, x4, y4); canvas.drawPath(path, mPaint); } postInvalidate(); } } //計(jì)算小球的X坐標(biāo) private float getSmallCenterX() { //此處控制速度 time = time + 2.5f; return mWidth / 2 + distance * (float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(time)); }}“精心”畫(huà)了一張圖,對(duì)代碼做了說(shuō)明。
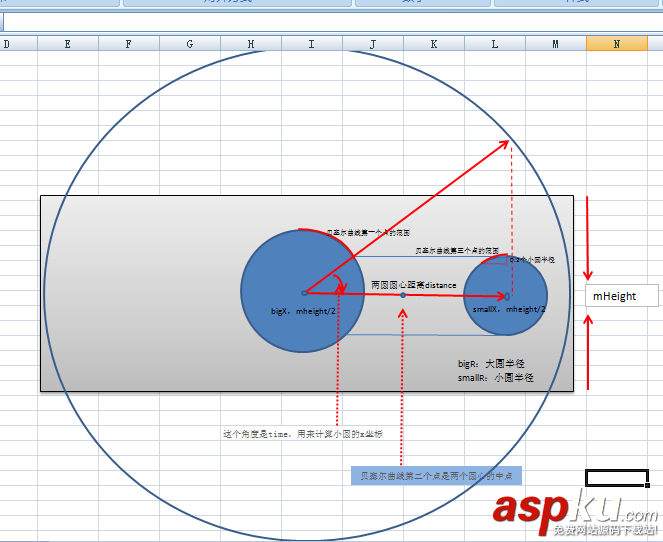
在代碼中使用
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="@color/white" tools:context="top.greendami.greendami.MainActivity"> <top.greendami.greendami.PPView android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:layout_width="400dp" android:layout_height="80dp" /></RelativeLayout>
總結(jié)
以上就是這篇文章的全部?jī)?nèi)容了,希望本文的內(nèi)容對(duì)大家的學(xué)習(xí)或者工作具有一定的參考學(xué)習(xí)價(jià)值,如果有疑問(wèn)大家可以留言交流,謝謝大家對(duì)VEVB武林網(wǎng)的支持。
新聞熱點(diǎn)
疑難解答
圖片精選
網(wǎng)友關(guān)注