前言
Nginx upstream與后端的連接默認為短連接,通過HTTP/1.0向后端發起連接,并把請求的"Connection" header設為"close"。Nginx與前端的連接默認為長連接,一個用戶跟Nginx建立連接之后,通過這個長連接發送多個請求。如果Nginx只是作為reverse proxy的話,可能一個用戶連接就需要多個向后端的短連接。如果后端的服務器(源站或是緩存服務器)處理并發連接能力不強的話,就可能導致瓶頸的出現。
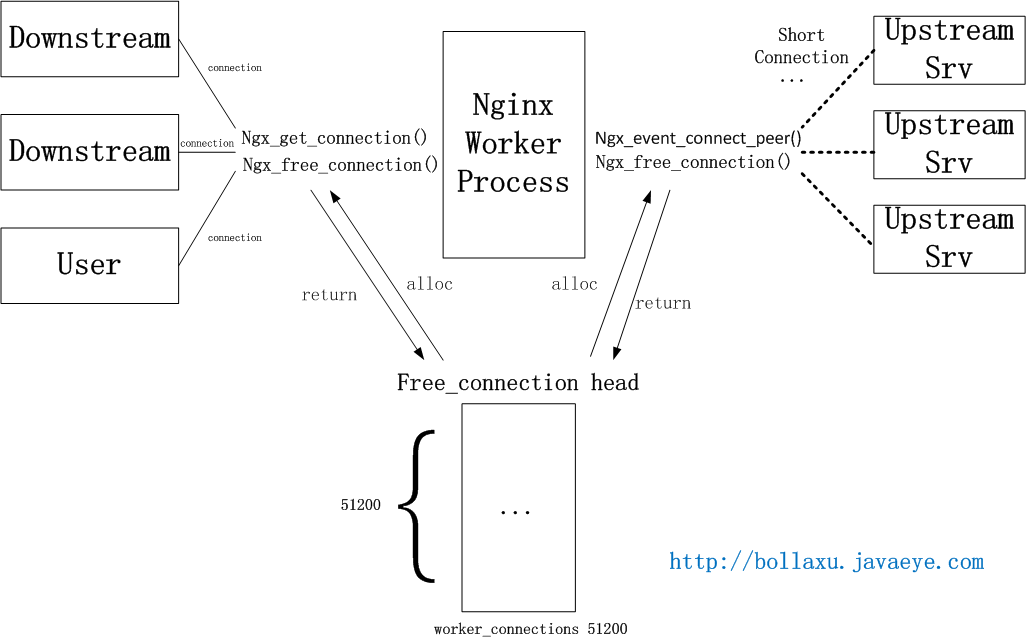
Nginx目前的upstream連接建立和獲取的機制如下圖。Nginx會在一開始創建connection pool(進程間不共享,可以避免鎖),提供給所有向前/后的連接。
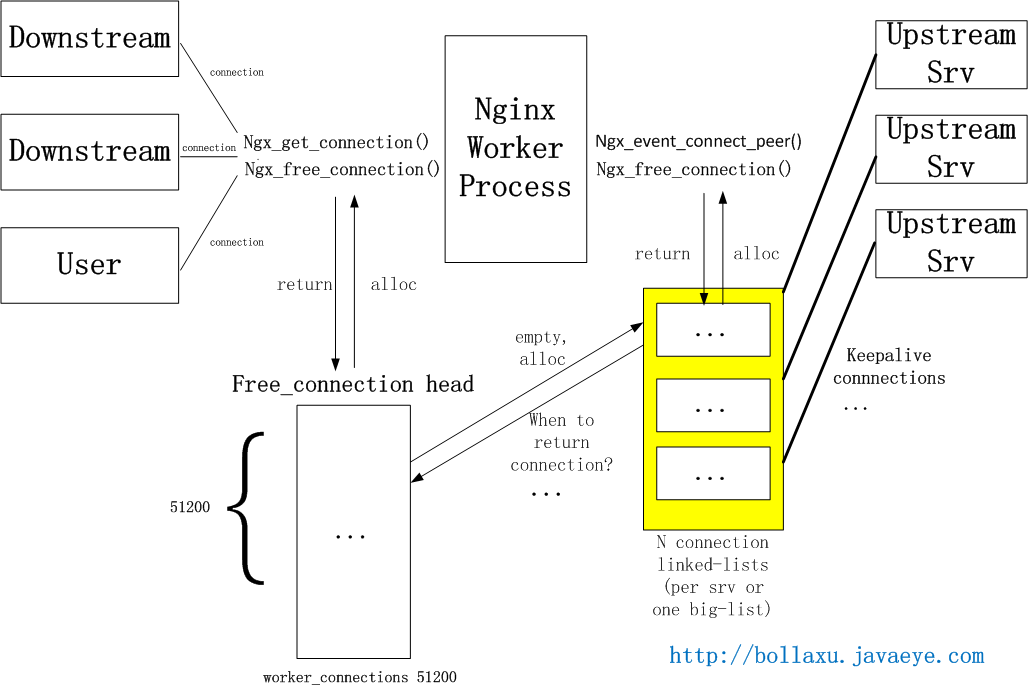
如果要實現upstream長連接,則每個進程需要另外一個connection pool,里面都是長連接。一旦與后端服務器建立連接,則在當前請求連接結束之后不會立即關閉連接,而是把用完的連接保存在一個keepalive connection pool里面,以后每次需要建立向后連接的時候,只需要從這個連接池里面找,如果找到合適的連接的話,就可以直接來用這個連接,不需要重新創建socket或者發起connect()。這樣既省下建立連接時三次握手的時間消耗,又可以避免TCP連接的slow start。如果在keepalive連接池找不到合適的連接,那就按照原來的步驟重新建立連接。假設連接查找時間可以忽略不計,那么這種方法肯定是有益而無害的(當然,需要少量額外的內存)。
具體如何來設計這個keepalive connection pool,不同人有不同的選擇。比如Nginx目前的第三方模塊upstream keepalive(作者Maxim Dounin)使用了一個queue來做。因為upstream的服務器很可能是多個,所以可能當保持的連接數多的時候,查找的時間可能會較長。可以給每個upstream服務器都分配一個pool(queue),縮短查找時間。但是總體來說內存操作很快,影響不會很大。upstream keepalive模塊目前只支持memcached,但是可以重用其代碼來達到對http upstream的長連接。由于Nginx作者之前沒有考慮upstream的長連接,所以在設計上要把http upstream keepalive模塊化可能比較難,只能通過手動修改代碼來做到。
一個完整的讓upstream支持長連接的配置示例如下:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
client_max_body_size 20M;
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
proxy_buffer_size 64k;
proxy_buffers 32 32k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 128k;
upstream aauCfg_backend {
server 127.0.0.1:97;
keepalive 16;
}
upstream HFC_backend {
server 127.0.0.1:8090;
keepalive 16;
}
upstream manager_backend {
server 127.0.0.1:8095;
keepalive 16;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
root html/tools;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real_IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
location / {
if (!-e $request_filename) {
#rewrite ^/(.*)$ /index.php/$1 last;
#break;
rewrite ^/(.*)$ /index.php/$1;
}
}
location ——* /.(ico|css|js|gif|jpe?g|png)(/?[0-9]+)?$ {
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
location ^—— /aauCfg/ {
#proxy_pass http://$remote_addr:97$request_uri;
proxy_pass http://aauCfg_backend;
}
location ^—— /HFC/ {
#proxy_pass http://$remote_addr:8090$request_uri;
proxy_pass http://HFC_backend;
}
location ^—— /manager/ {
#proxy_pass http://$remote_addr:8095$request_uri;
proxy_pass http://manager_backend;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location —— /.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location —— /.php$ {
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
location —— .php
{
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi.conf;
include fastcgi_params;
#定義變量 $path_info ,用于存放pathinfo信息
set $path_info "";
#定義變量 $real_script_name,用于存放真實地址
set $real_script_name $fastcgi_script_name;
#如果地址與引號內的正則表達式匹配
if ($fastcgi_script_name —— "^(.+?/.php)(/.+)$") {
#將文件地址賦值給變量 $real_script_name
set $real_script_name $1;
#將文件地址后的參數賦值給變量 $path_info
set $path_info $2;
}
#配置fastcgi的一些參數
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$real_script_name;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_NAME $real_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $path_info;
}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location —— //.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}