Python 的內存管理架構(Objects/obmalloc.c):
代碼如下:
_____ ______ ______ ________
[ int ] [ dict ] [ list ] ... [ string ] Python core |
+3 | <----- Object-specific memory -----> | <-- Non-object memory --> |
_______________________________ | |
[ Python's object allocator ] | |
+2 | ####### Object memory ####### | <------ Internal buffers ------> |
______________________________________________________________ |
[ Python's raw memory allocator (PyMem_ API) ] |
+1 | <----- Python memory (under PyMem manager's control) ------> | |
__________________________________________________________________
[ Underlying general-purpose allocator (ex: C library malloc) ]
0 | <------ Virtual memory allocated for the python process -------> |
0. C語言庫函數提供的接口
1. PyMem_*家族,是對 C中的 malloc、realloc和free 簡單的封裝,提供底層的控制接口。
2. PyObject_* 家族,高級的內存控制接口。
3. 對象類型相關的管理接口
PyMem_*
PyMem_家族:低級的內存分配接口(low-level memory allocation interfaces)
Python 對C中的 malloc、realloc和free 提供了簡單的封裝:
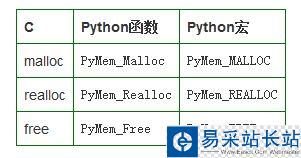
為什么要這么多次一舉:
不同的C實現對于malloc(0)產生的結果有會所不同,而PyMem_MALLOC(0)會轉成malloc(1). 不用的C實現的malloc與free混用會有潛在的問題。python提供封裝可以避免這個問題。 Python提供了宏和函數,但是宏無法避免這個問題,故編寫擴展是應避免使用宏源碼:
Include/pymem.h#define PyMem_MALLOC(n) ((size_t)(n) > (size_t)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX ? NULL / : malloc((n) ? (n) : 1))#define PyMem_REALLOC(p, n) ((size_t)(n) > (size_t)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX ? NULL / : realloc((p), (n) ? (n) : 1))#define PyMem_FREE free Objects/object.c/* Python's malloc wrappers (see pymem.h) */void *PyMem_Malloc(size_t nbytes){ return PyMem_MALLOC(nbytes);}...
新聞熱點
疑難解答