利用Opencv中的Houghline方法進行直線檢測—python語言
這是給Python部落翻譯的文章,請在這里看原文。
在圖像處理中,霍夫變換用來檢測任意能夠用數學公式表達的形狀,即使這個形狀被破壞或者有點扭曲。
下面我們將看到利用HoughLine算法來闡述霍夫變化進行直線檢測的原理,把此算法應用到特點圖像的邊緣檢測是可取的。邊緣檢測方法請參考這篇文章–邊緣檢測。
Houghline算法基礎
直線可以表示為y=mx+c,或者以極坐標形式表示為r=xcosθ+ysinθ,其中r是原點到直線的垂直距離,θ是水平軸順時針方向到垂直線的夾角(這個方向取決于坐標的形式,在OpenCV就是采用這種極坐標形式)。
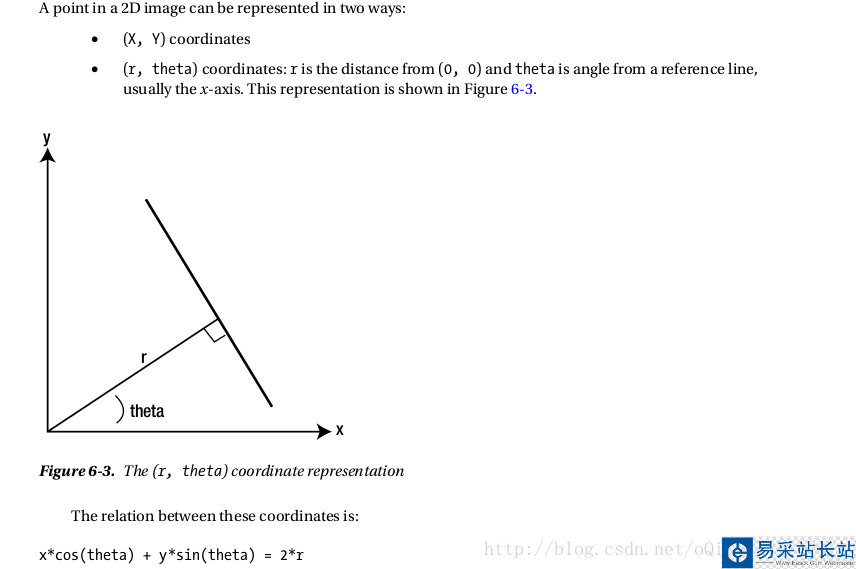
因此任意的曲線都可以用兩個參數(r,θ)表示。
HoughLine算法原理:
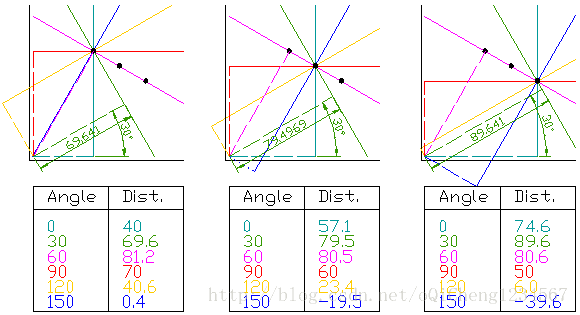
首先建立一個二維的數組或者累加器(用來保存這兩個參數),并初始化為零; 這個二維數組的行代表不同的r,而列代表角度θ; 數組的大小取決于算法的精度。假設所需角度的精度精確到1∘,那么就需要180列(直線的最大角度是180)。 對于r,最大的可能距離是圖像的對角長度,因此若需要一個像素的精度,那么需要把行數設為圖像對角線的長度。例子:
假設一幅100x100的圖像,在圖像中間有一條水平直線。設直線的第一個點的坐標為(x,y),在直線方程中,令參數θ=0,12,⋯,180,觀查參數r變化。對每一個參數對(r,θ),在累加器中將(r,θ)對應的單元格中的值遞增1,比如現在在累加器中,某個單元(50,90)的值等于1,其它的值也如此。
對于直線上的第二個點,重復上述操作。將得到的參數對(r,θ)的對應值繼續遞增,然后(50,90)對應的值等于2。實現上我們是對參數對(r,θ)進行投票,對直線上的每一個點重復上述操作,對每一個點,單元格(50,90)對應的值會遞增,或者說投票給參數對(50,90),而會或者不會投票給其它參數對。以這種方式,最后單元格(50,90)的值將會是最大的值。然后搜索累加器的最大值,將會找到參數對(50,90)。也就是說,在圖像中找到了到原點距離為50,角度為90的一條直線。
上述算法的過程被封裝成OpenCV函數cv2.HoughLines(),函數返回(r,θ)的一個數組,其中r的單位為像素,θ的單位為弧度。
# Python program to illustrate HoughLine# method for line detectionimport cv2import numpy as np# Reading the required image in # which operations are to be done. # Make sure that the image is in the same # directory in which this python program isimg = cv2.imread('xyz.jpg')# Convert the img to grayscalegray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# Apply edge detection method on the imageedges = cv2.Canny(gray,50,150,apertureSize = 3)# This returns an array of r and theta valueslines = cv2.HoughLines(edges,1,np.pi/180, 200)# The below for loop runs till r and theta values # are in the range of the 2d arrayfor r,theta in lines[0]: # Stores the value of cos(theta) in a a = np.cos(theta) # Stores the value of sin(theta) in b b = np.sin(theta) # x0 stores the value rcos(theta) x0 = a*r # y0 stores the value rsin(theta) y0 = b*r # x1 stores the rounded off value of (rcos(theta)-1000sin(theta)) x1 = int(x0 + 1000*(-b)) # y1 stores the rounded off value of (rsin(theta)+1000cos(theta)) y1 = int(y0 + 1000*(a)) # x2 stores the rounded off value of (rcos(theta)+1000sin(theta)) x2 = int(x0 - 1000*(-b)) # y2 stores the rounded off value of (rsin(theta)-1000cos(theta)) y2 = int(y0 - 1000*(a)) # cv2.line draws a line in img from the point(x1,y1) to (x2,y2). # (0,0,255) denotes the colour of the line to be #drawn. In this case, it is red. cv2.line(img,(x1,y1), (x2,y2), (0,0,255),2)# All the changes made in the input image are finally# written on a new image houghlines.jpgcv2.imwrite('houghlines3.jpg', img)
新聞熱點
疑難解答