本文實例講述了Python實現的多線程同步與互斥鎖功能。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
#! /usr/bin/env python#coding=utf-8import threadingimport time'''#1、不加鎖num = 0class MyThread(threading.Thread): def run(self): global num time.sleep(1) #一定要sleep!!! num = num + 1 msg = self.name + ' num is ---- ' + str(num) print msgdef test(): for i in range(10): s = MyThread() #實例化一個Thread對象,每個Thread對象代表著一個線程 s.start() #通過start()方法,開始線程活動'''#'''class MyThread(threading.Thread): def run(self): for i in range(3): time.sleep(1) msg = self.name+' @ '+str(i) print msgdef test(): for i in range(5): t = MyThread() t.start()#''''''#2、加鎖num = 0 #多個線程共享操作的數據mu = threading.Lock() #創建一個鎖class MyThread(threading.Thread): def run(self): global num time.sleep(1) if mu.acquire(True): #獲取鎖狀態,一個線程有鎖時,別的線程只能在外面等著 num = num + 1 msg = self.name + ' num is ---- ' + str(num) print msg mu.release() #釋放鎖def test(): for i in range(10): s = MyThread() s.start()'''if __name__ == '__main__': test()
運行結果:
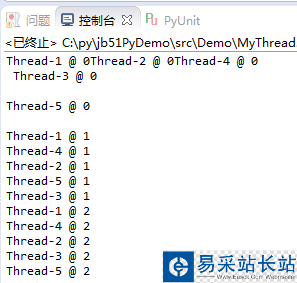
再分別運行注釋中的每一部分代碼:
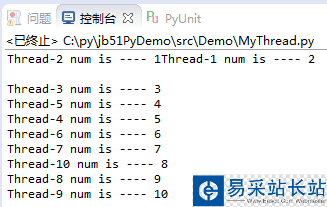
1. 不加鎖:
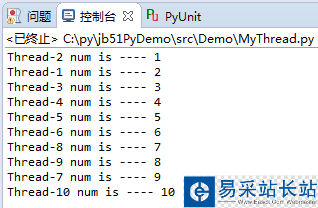
2. 加鎖:
更多關于Python相關內容感興趣的讀者可查看本站專題:《Python進程與線程操作技巧總結》、《Python Socket編程技巧總結》、《Python數據結構與算法教程》、《Python函數使用技巧總結》、《Python字符串操作技巧匯總》、《Python入門與進階經典教程》及《Python文件與目錄操作技巧匯總》
希望本文所述對大家Python程序設計有所幫助。
新聞熱點
疑難解答