前言
App自動化測試中有兩個很重要的操作,屏幕滑動與繪制手勢密碼。目前很多App在啟動時,都存在啟動時的引導動畫或者加載上下文內容時需要手動上滑或者下滑加載頁面,所以在自動化測試的過程中模擬手的滑動操作看起來就很重要了;第二個比較重要的是模擬手動繪制九宮格完成手勢密碼的設置,這種手勢密碼在我了解的范圍內,大多在金融類的app中最常見,還有一些對用戶信息保密性較好的app中,所以,模擬繪制手勢密碼也是app自動化測試中必須掌握的操作,那么接下來我們就開始講解兩種操作該如何實現, 在進入正題之前,你還應該知道,手機中橫縱坐標的原點是從屏幕的左上角頂點(0, 0)的位置開始的
滑動屏幕
swipe方法
模擬滑動屏幕的操作,我們通過swipe方法實現,先看一下這個方法的源代碼
def swipe(self, start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, duration=None): """Swipe from one point to another point, for an optional duration. Args: start_x (int): x-coordinate at which to start start_y (int): y-coordinate at which to start end_x (int): x-coordinate at which to stop end_y (int): y-coordinate at which to stop duration (:obj:`int`, optional): time to take the swipe, in ms. Usage: driver.swipe(100, 100, 100, 400) Returns: `WebElement` """ # `swipe` is something like press-wait-move_to-release, which the server # will translate into the correct action action = TouchAction(self) action / .press(x=start_x, y=start_y) / .wait(ms=duration) / .move_to(x=end_x, y=end_y) / .release() action.perform() return self
參數
start_x, start_y : 表示開始滑動時的初始坐標,也就是從哪里開始滑動
end_x, end_y : 表示滑動后的坐標,也就是滑動到哪里
duration: : 表示滑動過程的時間間隔,模擬操作時,我們最好設置個時間間隔,避免由于代碼運行太快,而真機或者模擬器反應比較慢,而操作失敗,單位以毫秒計算
通過源碼,我們發現swipe方法實際上是使用TouchAction實現的,這個類在后面我們仍然會使用,主要是模擬一些觸屏動作
實現思路
大家可以想象一下,平時我們滑動屏幕時,是如何操作的?例如向左滑動屏幕,我們往往是把手放在屏幕的右側,然后按住屏幕向左滑動,那么代碼如何知道我們從屏幕的哪個位置開始訥?那就是坐標了,我們可以先獲取屏幕的寬,高,然后按照它的比例計算鼠標的位置坐標,我這里取的起始坐標點為屏幕寬度的0.9倍,高度的0.5倍,大概就是我們實際中滑屏時手指的操作位置。大家可以根據下面播放的動畫觀察鼠標開始的大概位置和結束位置

接下來我們開始模擬動畫中鼠標的操作(人手的操作,我用的模擬器所以有鼠標)
首先我們通過get_window_size()方法獲取屏幕的寬和高(這個方法返回一個字典),然后計算鼠標的初始位置和結束為止
def get_phone_size(self): """獲取屏幕的大小""" width = self.driver.get_window_size()['width'] # 獲取屏幕的寬 height = self.driver.get_window_size()['height'] # 獲取屏幕的高 return width, height
通過模擬動畫不難看出,鼠標大概從起始點坐標(屏幕寬的3/4,高的1/2)位置滑動到結束點坐標(屏幕寬1/4,高1/2),ok,接下來通過swipe()方法實現滑動操作
def swipe_left(self, duration=300): """左滑""" width, height = self.get_phone_size start = width * 0.9, height * 0.5 end = width * 0.1, height * 0.5 return self.driver.swipe(*start, *end, duration) def swipe_right(self, duration=300): """右滑""" width, height = self.get_phone_size start = width * 0.9, height * 0.5 end = width * 0.1, height * 0.5 return self.driver.swipe(*start, *end, duration) def swipe_up(self, duration): """上滑""" width, height = self.get_phone_size start = width * 0.9, height * 0.5 end = width * 0.1, height * 0.5 return self.driver.swipe(*start, *end, duration) def swipe_down(self, duration): """下滑""" width, height = self.get_phone_size start = width * 0.9, height * 0.5 end = width * 0.1, height * 0.5 return self.driver.swipe(*start, *end, duration)
方法優化
以上每一個方法調用一次只能滑動一次,而且不同的滑動方向需要調用不同的方法,使用時比較麻煩。所以我們可以優化一下代碼,通過調用一個函數實現不同次數,不同方向的滑動
使用for循環實現連續的滑動,引入direction參數,結合字典及反射機制,實現根據不同的參數執行不同滑動方向的方法,傳遞num參數控制滑動的次數,具體代碼如下
def skip_welcome_page(self, direction, num=3): """ 滑動頁面跳過引導動畫 :param direction: str 滑動方向,left, right, up, down :param num: 滑動次數 :return: """ direction_dic = { "left": "swipe_left", "right": "swipe_right", "up": "swipe_up", "down": "swipe_down" } time.sleep(3) if hasattr(self, direction_dic[direction]): for _ in range(num): getattr(self, direction_dic[direction])() # 使用反射執行不同的滑動方法 else: raise ValueError("參數{}不存在, direction可以為{}任意一個字符串". format(direction, direction_dic.keys()))以上就是所有滑動屏幕的操作了,具體效果,我們后面再看(你也可以先試試)
手勢密碼
TouchAction類
模擬手勢密碼的繪制我們使用TouchAction類,這個類提供了短按壓press()方法,wait()方法,move_to()方法,release()方法,perform()方法等常用方法,下面我簡單說明一下這幾個方法的作用
press(element, x, y) : 其中element參數是一個元素對象,當element不為空時,x和y必須位None,如果element為None時,x如果不為None,那么y也不能位None,也就是說在安卓操作系統中,element和(x,y)必要傳遞一個,蘋果系統可以不傳,這里不做介紹
wait(duration) : duration是時間,以毫秒為單位,這個方法的作用是等待一段時間,和sleep的作用類似,唯一區別sleep不能被TouchAtion對象訪問
release() : 這個方法的作用是結合press等按壓動作使用的,表示抬起動作
perform():這個方法的作用是使所有的按壓及等待,release等動作生效
實現思路
模擬大多app中的手勢設置密碼操作會遇見兩種情況,一種是9宮格中每一個點的元素都可以通過定位表達式定位到,另一種是每個點無法通過定位表達式定位到的,只能定位到整體9宮格元素,每個點只能通過獲取坐標的方式定位,那么我們今天模擬繪制手勢密碼的情況就是第二種,如果這種掌握了,那么第一種更簡單,下面我們分析一下該如何獲取每一個點的坐標,先來看下面的圖
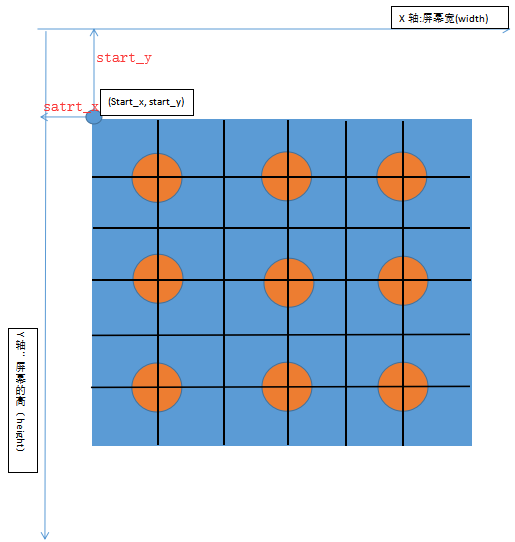
上圖中的x軸,y軸是手機的坐標表示方式,請區別數學中的二維坐標,其中x軸方向表示手機屏幕的寬度width,y軸方向表示屏幕的高度height,原點為(0, 0); 藍色方框代表9宮格手勢操作的整體元素(內部包含9個點),start_x, start_y 代表9宮格元素的起始坐標點,start_x也是9宮格起始點距離y軸的距離,start_y也是9宮格起始點距離x軸的距離,請大家一定理解這幾個值的關系,下面我們可以通過WebElement對象的rect方法獲取9宮格元素的寬,高及起始點坐標
def get_element_size_location(element): width = element.rect["width"] # 9宮格元素的寬度 height = element.rect["height"] # 9宮格坐標的高度 # 9宮格元素的起始坐標點 start_x = element.rect["x"] start_y = element.rect["y"] return width, height, start_x, start_y
除了使用rect方法外,你還可以使用location和size方法分別獲取元素的起始點坐標和寬,高,兩個方法同樣返回字典
element.location ->{"x": start_x, "y": start_y}element.size ->{"width": width, "height": height}接下來我們通過9宮格元素的width,height,start_x, start_y分別計算每個點的坐標, 我們按照上圖,把9宮格元素的width和height分別等分為6等分
前3個點(1, 2, 3)的坐標分別是
width, height, start_x, start_y = self.get_element_size_location(element)point_1 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)}point_2 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)}point_3 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)}中間3個點(4, 5, 6)的坐標分別為
point_4 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)}point_5 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)}point_6 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)}最后3個點(7, 8, 9)的坐標分別為
point_7 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)}point_8 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)}point_9 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)}下面我們使用TouchAction類中的move_to,wait,release,perform方法實現從一個點移動到另一個點,進而實現模擬手勢密碼的連線操作(鏈接1-2-3-6-9)
TouchAction(driver).press(x=point_1["x"], y=point_1["y"]).wait(300)/ .move_to(x=point_2["x"], y=point_2["y"]).wait(500)/ .move_to(x=point_3["x"], y=point_3["y"]).wait(500)/ .move_to(x=point_6["x"], y=point_6["y"]).wait(500)/ .move_to(x=point_9["x"], y=point_9["y"]).wait(500).release().perform()
完整代碼
不包含滑動屏幕的代碼
base.py
"""------------------------------------@Time : 2019/8/6 20:22@Auth : linux超@File : base.py@IDE : PyCharm@Motto: Real warriors,dare to face the bleak warning,dare to face the incisive error!@QQ : 28174043@qq.com@GROUP: 878565760------------------------------------"""from appium.webdriver import WebElementfrom appium.webdriver.common.touch_action import TouchActionfrom appium.webdriver.webdriver import WebDriverfrom selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWaitfrom selenium.common.exceptions import NoSuchElementException, TimeoutExceptionclass Base(object): def __init__(self, driver: WebDriver): self.driver = driver @staticmethod def get_element_size_location(element): width = element.rect["width"] height = element.rect["height"] start_x = element.rect["x"] start_y = element.rect["y"] return width, height, start_x, start_y def gesture_password(self, element: WebElement): width, height, start_x, start_y = self.get_element_size_location(element) point_1 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)} point_2 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)} point_3 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)} point_4 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)} point_5 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)} point_6 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)} point_7 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)} point_8 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)} point_9 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)} TouchAction(self.driver).press(x=point_1["x"], y=point_1["y"]).wait(300) / .move_to(x=point_2["x"], y=point_2["y"]).wait(500) / .move_to(x=point_3["x"], y=point_3["y"]).wait(500) / .move_to(x=point_6["x"], y=point_6["y"]).wait(500) / .move_to(x=point_9["x"], y=point_9["y"]).wait(500).release().perform() def find_element(self, locator: tuple, timeout=30) -> WebElement: wait = WebDriverWait(self.driver, timeout) try: element = wait.until(lambda driver: driver.find_element(*locator)) return element except (NoSuchElementException, TimeoutException): print('no found element {} by {}', format(locator[1], locator[0]))if __name__ == '__main__': pass測試代碼
test_gesture_password.pyimport timeimport unittestfrom appium import webdriverfrom appium.webdriver.common.mobileby import MobileByfrom base import Baseclass TestGesture(unittest.TestCase): def setUp(self): desired = { "automationName": "uiautomator1", "platformName": "Android", "platformVersion": '5.1.1', "deviceName": "127.0.0.1:62001", "appPackage": "com.xxzb.fenwoo", "appActivity": "com.xxzb.fenwoo.activity.addition.WelcomeActivity", "app": r"D:/AppAutoTest/appPackage/Future-release-2018.apk", "unicodeKeyboard": True, # 屏蔽鍵盤 "resetKeyboard": True } self.driver = webdriver.Remote(command_executor="http://127.0.0.1:4723/wd/hub", desired_capabilities=desired) self.base = Base(self.driver) def test_gesture_password(self): # 直接切換到手勢密碼頁面 self.driver.start_activity(app_package="com.xxzb.fenwoo", app_activity=".activity.user.CreateGesturePwdActivity") commit_btn = (MobileBy.ID, 'com.xxzb.fenwoo:id/right_btn') password_gesture = (MobileBy.ID, 'com.xxzb.fenwoo:id/gesturepwd_create_lockview') element_commit = self.base.find_element(commit_btn) element_commit.click() # 9宮格元素 password_element = self.base.find_element(password_gesture) self.base.gesture_password(password_element) time.sleep(5) # 為了看效果 def tearDown(self): self.driver.quit()if __name__ == '__main__': unittest.main()
以上就是完整的模擬手勢密碼操作的代碼, 但是問題來了 , 我這里執行的時候不成功,很尷尬,但是我確實看到過別人通過這種獲取每個點的坐標,從一個點的坐標移動到另一個點的坐標的方式成功畫線了,當然你可以先試試能不能成功再往下看!
方法重寫
如果上邊的方式你也不成功,那么就試試下面的方法吧,原理是一樣的,主要不同點在,move_to方法傳遞的不是每個點的坐標,而是相對點的坐標,也就是從一個點移動到另一個點的距離坐標,例如點1的坐標為(360, 579), 點2的坐標為(580, 579), 那么移動的距離應該是橫向220,縱向為0, 傳遞的參數應該是這樣的move_to(x=220, y=0)(這里傳遞的參數叫做相對位置坐標,但是move_to的源碼就是按照我之前的寫法傳參的,具體為啥,我也不得而知了),修改部分代碼如下
TouchAction(self.driver).press(x=point_1["x"], y=point_1["y"]).wait(300) / .move_to(x=point_2["x"]-point_1["x"], y=point_2["y"]-point_1["y"]).wait(500) / .move_to(x=point_3["x"]-point_2["x"], y=point_3["y"]-point_2["y"]).wait(500) / .move_to(x=point_6["x"]-point_3["x"], y=point_6["y"]-point_3["y"]).wait(500) / .move_to(x=point_9["x"]-point_6["x"], y=point_9["y"]-point_6["y"]).wait(500).release().perform()
相對坐標的計算方法:用后一個目標點坐標減去前一個點的坐標即為相對坐標,你可以把這個段代碼替換一下,你會發現確實成功了
代碼優化
上述代碼你會發現, 每次繪制的只能是同一個密碼,如果我想繪制不同的密碼,那么就必須修改繪制時傳遞的坐標,作為一枚優秀的程序員怎么可以這樣訥?沖這句話,我就必須得想辦法做到繪制任何密碼組合的情況。我的需求是,當我給繪制函數getsture_password()傳遞不同密碼時(例如這樣的方式getsture_password(1, 2, 3, 6, 9))那么程序應該幫我把1-2-3-6-9鏈接起來,所以我想到了使用字典,把每個數字分別對應每一個坐標點,像下面這樣
def get_password_location(self, element: WebElement) -> dict: width, height, start_x, start_y = self.get_element_size_location(element) point_1 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)} point_2 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)} point_3 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)} point_4 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)} point_5 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)} point_6 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)} point_7 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)} point_8 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)} point_9 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)} keys = { 1: point_1, 2: point_2, 3: point_3, 4: point_4, 5: point_5, 6: point_6, 7: point_7, 8: point_8, 9: point_9 } return keys然后我通過另一個方法來實現繪制連線的功能
def gesture_password(self, element: WebElement, *pwd): # pwd是個元組,pwd[0]表示第一個密碼 """手勢密碼: 直接輸入需要鏈接的點對應的數字,最多9位 pwd: 傳你想連接的點構成的密碼,如:1, 2, 3, 6, 9 """ if len(pwd) > 9: raise ValueError("需要設置的密碼不能超過9位!") keys_dict = self.get_password_location(element) # 9個點的坐標組成的字典 start_point = "TouchAction(self.driver).press(x={0}, y={1}).wait(200)"./ # keys_dict[pwd[0]] 得到第一位密碼數字對應的坐標的字典 format(keys_dict[pwd[0]]["x"], keys_dict[pwd[0]]["y"]) # 起始點的坐標 for index in range(len(pwd)-1): # 0,1,2,3 follow_point = ".move_to(x={0}, y={1}).wait(200)"./ format(keys_dict[pwd[index+1]]["x"] - keys_dict[pwd[index]]["x"], keys_dict[pwd[index+1]]["y"] - keys_dict[pwd[index]]["y"]) # 后續的點坐標 start_point = start_point + follow_point # 把起始點的表達式和后續鏈接的點表達式鏈接在一起組成一個模擬連線的完整過程 full_point = start_point + ".release().perform()" # 完整的過程通過.release().perform()使其生效 return eval(full_point) # 執行一串表達式比較難理解的地方,我已經詳細注釋了,當然,你可以復制我的代碼先驗證能否繪制成功再分析代碼的實現原理
所有代碼
修改后的繪制手勢密碼代碼&滑屏代碼
"""------------------------------------@Time : 2019/8/6 20:45@Auth : linux超@File : base.py@IDE : PyCharm@Motto: Real warriors,dare to face the bleak warning,dare to face the incisive error!@QQ : 28174043@qq.com@GROUP: 878565760------------------------------------"""import timefrom appium.webdriver import WebElementfrom appium.webdriver.common.touch_action import TouchActionfrom appium.webdriver.webdriver import WebDriverfrom selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWaitfrom selenium.common.exceptions import NoSuchElementException, TimeoutExceptionclass Base(object): def __init__(self, driver: WebDriver): self.driver = driver @property def get_phone_size(self): """獲取屏幕的大小""" width = self.driver.get_window_size()['width'] height = self.driver.get_window_size()['height'] return width, height def swipe_left(self, duration=300): """左滑""" width, height = self.get_phone_size start = width * 0.9, height * 0.5 end = width * 0.1, height * 0.5 return self.driver.swipe(*start, *end, duration) def swipe_right(self, duration=300): """右滑""" width, height = self.get_phone_size start = width * 0.1, height * 0.5 end = width * 0.9, height * 0.5 return self.driver.swipe(*start, *end, duration) def swipe_up(self, duration): """上滑""" width, height = self.get_phone_size start = width * 0.5, height * 0.9 end = width * 0.5, height * 0.1 return self.driver.swipe(*start, *end, duration) def swipe_down(self, duration): """下滑""" width, height = self.get_phone_size start = width * 0.5, height * 0.1 end = width * 0.5, height * 0.9 return self.driver.swipe(*start, *end, duration) def skip_welcome_page(self, direction, num=3): """ 滑動頁面跳過引導動畫 :param direction: str 滑動方向,left, right, up, down :param num: 滑動次數 :return: """ direction_dic = { "left": "swipe_left", "right": "swipe_right", "up": "swipe_up", "down": "swipe_down" } time.sleep(3) if hasattr(self, direction_dic[direction]): for _ in range(num): getattr(self, direction_dic[direction])() # 使用反射執行不同的滑動方法 else: raise ValueError("參數{}不存在, direction可以為{}任意一個字符串". format(direction, direction_dic.keys())) @staticmethod def get_element_size_location(element): width = element.rect["width"] height = element.rect["height"] start_x = element.rect["x"] start_y = element.rect["y"] return width, height, start_x, start_y def get_password_location(self, element: WebElement) -> dict: width, height, start_x, start_y = self.get_element_size_location(element) point_1 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)} point_2 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)} point_3 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 1)} point_4 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)} point_5 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)} point_6 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 3)} point_7 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 1), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)} point_8 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 3), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)} point_9 = {"x": int(start_x + width * (1 / 6) * 5), "y": int(start_y + height * (1 / 6) * 5)} keys = { 1: point_1, 2: point_2, 3: point_3, 4: point_4, 5: point_5, 6: point_6, 7: point_7, 8: point_8, 9: point_9 } return keys def gesture_password(self, element: WebElement, *pwd): """手勢密碼: 直接輸入需要鏈接的點對應的數字,最多9位 pwd: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9 """ if len(pwd) > 9: raise ValueError("需要設置的密碼不能超過9位!") keys_dict = self.get_password_location(element) start_point = "TouchAction(self.driver).press(x={0}, y={1}).wait(200)". / format(keys_dict[pwd[0]]["x"], keys_dict[pwd[0]]["y"]) for index in range(len(pwd) - 1): # 0,1,2,3 follow_point = ".move_to(x={0}, y={1}).wait(200)". / format(keys_dict[pwd[index + 1]]["x"] - keys_dict[pwd[index]]["x"], keys_dict[pwd[index + 1]]["y"] - keys_dict[pwd[index]]["y"]) start_point = start_point + follow_point full_point = start_point + ".release().perform()" return eval(full_point) def find_element(self, locator: tuple, timeout=30) -> WebElement: wait = WebDriverWait(self.driver, timeout) try: element = wait.until(lambda driver: driver.find_element(*locator)) return element except (NoSuchElementException, TimeoutException): print('no found element {} by {}', format(locator[1], locator[0]))if __name__ == '__main__': pass"""------------------------------------@Time : 2019/8/6 20:47@Auth : linux超@File : test.py@IDE : PyCharm@Motto: Real warriors,dare to face the bleak warning,dare to face the incisive error!@QQ : 28174043@qq.com@GROUP: 878565760------------------------------------"""import timeimport unittestfrom appium import webdriverfrom appium.webdriver.common.mobileby import MobileByfrom base import Baseclass TestGesture(unittest.TestCase): def setUp(self): desired = { "automationName": "uiautomator1", "platformName": "Android", "platformVersion": '5.1.1', "deviceName": "127.0.0.1:62001", "appPackage": "com.xxzb.fenwoo", "appActivity": "com.xxzb.fenwoo.activity.addition.WelcomeActivity", "app": r"D:/AppAutoTest/appPackage/Future-release-2018.apk", "unicodeKeyboard": True, # 屏蔽鍵盤 "resetKeyboard": True } self.driver = webdriver.Remote(command_executor="http://127.0.0.1:4723/wd/hub", desired_capabilities=desired) self.base = Base(self.driver) def test_gesture_password(self): self.base.skip_welcome_page('left', 3) # 滑動屏幕 time.sleep(3) # 為了看滑屏的效果 self.driver.start_activity(app_package="com.xxzb.fenwoo", app_activity=".activity.user.CreateGesturePwdActivity") commit_btn = (MobileBy.ID, 'com.xxzb.fenwoo:id/right_btn') password_gesture = (MobileBy.ID, 'com.xxzb.fenwoo:id/gesturepwd_create_lockview') element_commit = self.base.find_element(commit_btn) element_commit.click() password_element = self.base.find_element(password_gesture) self.base.gesture_password(password_element, 1, 2, 3, 6, 5, 4, 7, 8, 9) time.sleep(5) # 看效果 def tearDown(self): self.driver.quit()if __name__ == '__main__': unittest.main()測試效果
包含滑動屏幕
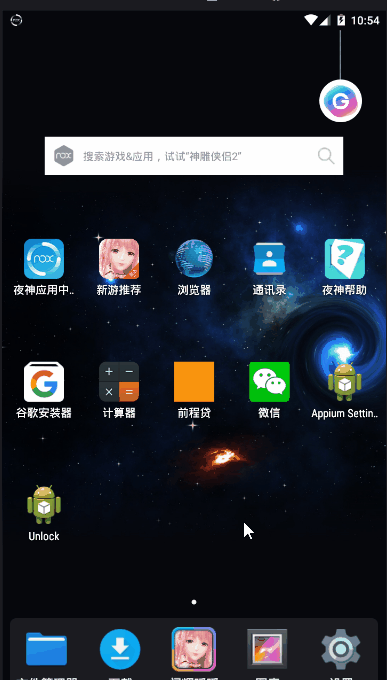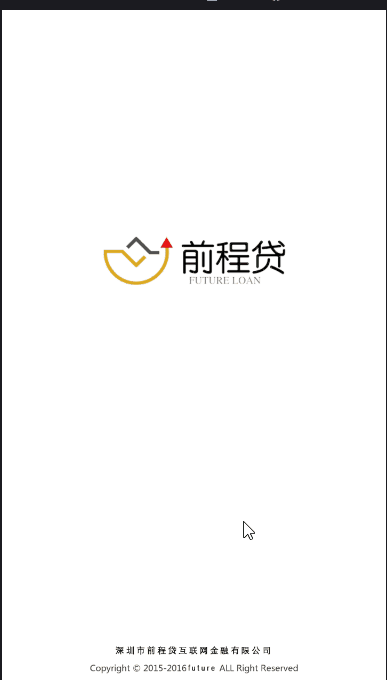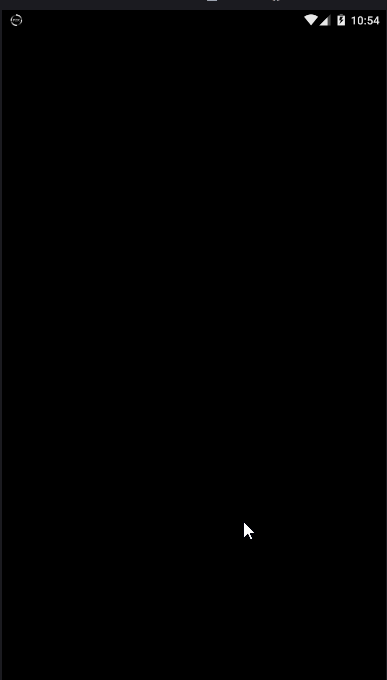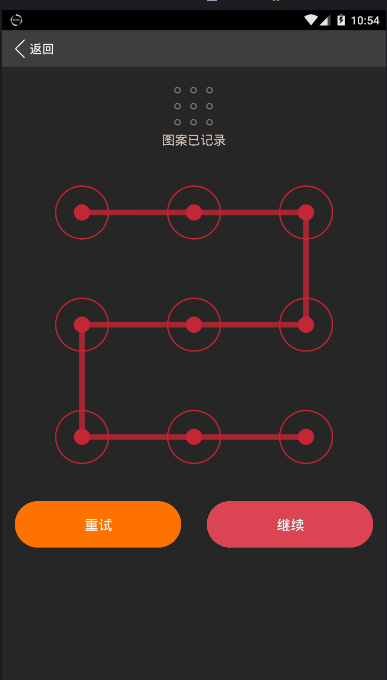
總結
最后,我們再總結一下完成所有的操作需要掌握的知識點
1.滑動屏幕時起始位置和結束位置應該從哪里開始與結束,如何獲取
2.滑動屏幕使用的swipe()方法如何使用
3.實現多次滑動方法的實現原理,這里用到了反射,其實使用if也可以實現一樣的效果,但是總感覺if有點low
4.9宮格起始位置與手機屏幕的關系及每個點的坐標如何計算
5.TouchAction類中的常用方法如何使用
6.理解繪制手勢密碼方法的封裝原理及思路
以上所述是小編給大家介紹的使用swipe方法模擬屏幕滑動與手勢密碼繪制,希望對大家有所幫助,如果大家有任何疑問請給我留言,小編會及時回復大家的。在此也非常感謝大家對武林網網站的支持!
如果你覺得本文對你有幫助,歡迎轉載,煩請注明出處,謝謝!
新聞熱點
疑難解答