本文實例講述了C語言二叉樹常見操作。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
一、基本概念
每個結(jié)點最多有兩棵子樹,左子樹和右子樹,次序不可以顛倒。
性質(zhì):
1、非空二叉樹的第n層上至多有2^(n-1)個元素。
2、深度為h的二叉樹至多有2^h-1個結(jié)點。
滿二叉樹:所有終端都在同一層次,且非終端結(jié)點的度數(shù)為2。
在滿二叉樹中若其深度為h,則其所包含的結(jié)點數(shù)必為2^h-1。
完全二叉樹:除了最大的層次即成為一顆滿二叉樹且層次最大那層所有的結(jié)點均向左靠齊,即集中在左面的位置上,不能有空位置。
對于完全二叉樹,設(shè)一個結(jié)點為i則其父節(jié)點為i/2,2i為左子節(jié)點,2i+1為右子節(jié)點。
二、存儲結(jié)構(gòu)
順序存儲:
將數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)存在一塊固定的數(shù)組中。
#define LENGTH 100typedef char datatype;typedef struct node{ datatype data; int lchild,rchild; int parent;}Node;Node tree[LENGTH];int length;int root;雖然在遍歷速度上有一定的優(yōu)勢,但因所占空間比較大,是非主流二叉樹。二叉樹通常以鏈?zhǔn)酱鎯Α?/p>
鏈?zhǔn)酱鎯Γ?/strong>
typedef char datatype;typedef struct BinNode{ datatype data; struct BinNode* lchild; struct BinNode* rchild;}BinNode;typedef BinNode* bintree; //bintree本身是個指向結(jié)點的指針三、二叉樹的遍歷
遍歷即將樹的所有結(jié)點訪問且僅訪問一次。按照根節(jié)點位置的不同分為前序遍歷,中序遍歷,后序遍歷。
前序遍歷:根節(jié)點->左子樹->右子樹
中序遍歷:左子樹->根節(jié)點->右子樹
后序遍歷:左子樹->右子樹->根節(jié)點
例如:求下面樹的三種遍歷
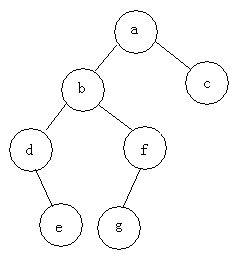
前序遍歷:abdefgc
中序遍歷:debgfac
后序遍歷:edgfbca
四、遍歷的實現(xiàn)
遞歸實現(xiàn)(以前序遍歷為例,其他的只是輸出的位置稍有不同)
void preorder(bintree t){ if(t){ printf("%c ",t->data); preorder(t->lchild); preorder(t->rchild); }}非遞歸的實現(xiàn)
因為當(dāng)遍歷過根節(jié)點之后還要回來,所以必須將其存起來。考慮到后進先出的特點,選用棧存儲。數(shù)量確定,以順序棧存儲。
#define SIZE 100typedef struct seqstack{ bintree data[SIZE]; int tag[SIZE]; //為后續(xù)遍歷準(zhǔn)備的 int top; //top為數(shù)組的下標(biāo)}seqstack;void push(seqstack *s,bintree t){ if(s->top == SIZE){ printf("the stack is full/n"); }else{ s->top++; s->data[s->top]=t; }}bintree pop(seqstack *s){ if(s->top == -1){ return NULL; }else{ s->top--; return s->data[s->top+1]; }}1、前序遍歷
void preorder_dev(bintree t){ seqstack s; s.top = -1; //因為top在這里表示了數(shù)組中的位置,所以空為-1 if(!t){ printf("the tree is empty/n"); }else{ while(t || s.stop != -1){ while(t){ //只要結(jié)點不為空就應(yīng)該入棧保存,與其左右結(jié)點無關(guān) printf("%c ",t->data); push(&s,t); t= t->lchild; } t=pop(&s); t=t->rchild; } }}2、中序遍歷
void midorder(bintree t){ seqstack s; s.top = -1; if(!t){ printf("the tree is empty!/n"); }else{ while(t ||s.top != -1){ while(t){ push(&s,t); t= t->lchild; } t=pop(&s); printf("%c ",t->data); t=t->rchild; } }}3、后序遍歷
因為后序遍歷最后還要要訪問根結(jié)點一次,所以要訪問根結(jié)點兩次。采取夾標(biāo)志位的方法解決這個問題。
這段代碼非常糾結(jié),對自己有信心的朋友可以嘗試獨立寫一下。反正我是寫了很長時間。邏輯不難,我畫了一張邏輯圖:
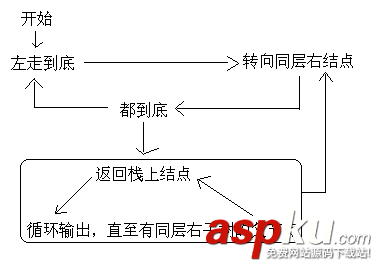
代碼:
void postorder_dev(bintree t){ seqstack s; s.top = -1; if(!t){ printf("the tree is empty!/n"); }else{ while(t || s.top != -1){ //棧空了的同時t也為空。 while(t){ push(&s,t); s.tag[s.top] = 0; //設(shè)置訪問標(biāo)記,0為第一次訪問,1為第二次訪問 t= t->lchild; } if(s.tag[s.top] == 0){ //第一次訪問時,轉(zhuǎn)向同層右結(jié)點 t= s.data[s.top]; //左走到底時t是為空的,必須有這步! s.tag[s.top]=1; t=t->rchild; }else { while (s.tag[s.top] == 1){ //找到棧中下一個第一次訪問的結(jié)點,退出循環(huán)時并沒有pop所以為其左子結(jié)點 t = pop(&s); printf("%c ",t->data); } t = NULL; //必須將t置空。跳過向左走,直接向右走 } } }}4、層次遍歷:即每一層從左向右輸出
元素需要儲存有先進先出的特性,所以選用隊列存儲。
隊列的定義:
#define MAX 1000typedef struct seqqueue{ bintree data[MAX]; int front; int rear;}seqqueue;void enter(seqqueue *q,bintree t){ if(q->rear == MAX){ printf("the queue is full!/n"); }else{ q->data[q->rear] = t; q->rear++; }}bintree del(seqqueue *q){ if(q->front == q->rear){ return NULL; }else{ q->front++; return q->data[q->front-1]; }}遍歷實現(xiàn)
void level_tree(bintree t){ seqqueue q; bintree temp; q.front = q.rear = 0; if(!t){ printf("the tree is empty/n"); return ; } enter(&q,t); while(q.front != q.rear){ t=del(&q); printf("%c ",t->data); if(t->lchild){ enter(&q,t->lchild); } if(t->rchild){ enter(&q,t->rchild); } }}5、利用前序遍歷的結(jié)果生成二叉樹
//遞歸調(diào)用,不存點,想的時候只關(guān)注于一個點,因為還會回來的,不要跟蹤程序運行,否則容易多加循環(huán)void createtree(bintree *t){ datatype c; if((c=getchar()) == '#') *t = NULL; else{ *t = (bintree)malloc(sizeof(BinNode)); (*t)->data = c; createtree(&(*t)->lchild); createtree(&(*t)->rchild); }}6、二叉樹的查找
bintree search_tree(bintree t,datatype x){ if(!t){ return NULL; } if(t->data == x){ return t; }else{ if(!search_tree(t->lchild,x)){ return search_tree(t->rchild,x); } return t; }}7、統(tǒng)計結(jié)點個數(shù)
int count_tree(bintree t){ if(t){ return (count_tree(t->lchild)+count_tree(t->rchild)+1); } return 0;}8、比較兩個樹是否相同
int is_equal(bintree t1,bintree t2){ if(!t1 && !t2){ //都為空就相等 return 1; } if(t1 && t2 && t1->data == t2->data){ //有一個為空或數(shù)據(jù)不同就不判斷了 if(is_equal(t1->lchild,t2->lchild)) if(is_equal(t1->rchild,t2->rchild)){ return 1; } } return 0;}9、求二叉樹的深度
int hight_tree(bintree t){ int h,left,right; if(!t){ return 0; } left = hight_tree(t->lchild); right = hight_tree(t->rchild); h = (left>right?left:right)+1; return h;}希望本文所述對大家C語言程序設(shè)計有所幫助。
新聞熱點
疑難解答